Brush DC Gear Motors: The Heartbeat of Many Devices
Brush DC gear motors, or brushed DC gear motors, are traditional yet versatile components widely used in various applications ranging from toys and household appliances to industrial equipment. These motors have been around for decades, and their popularity stems from their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
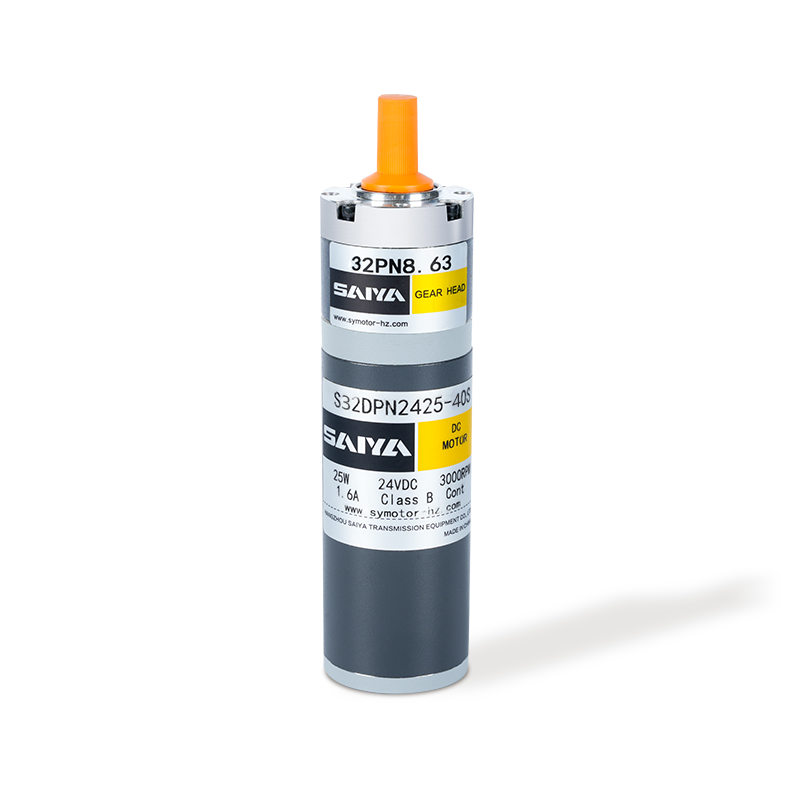
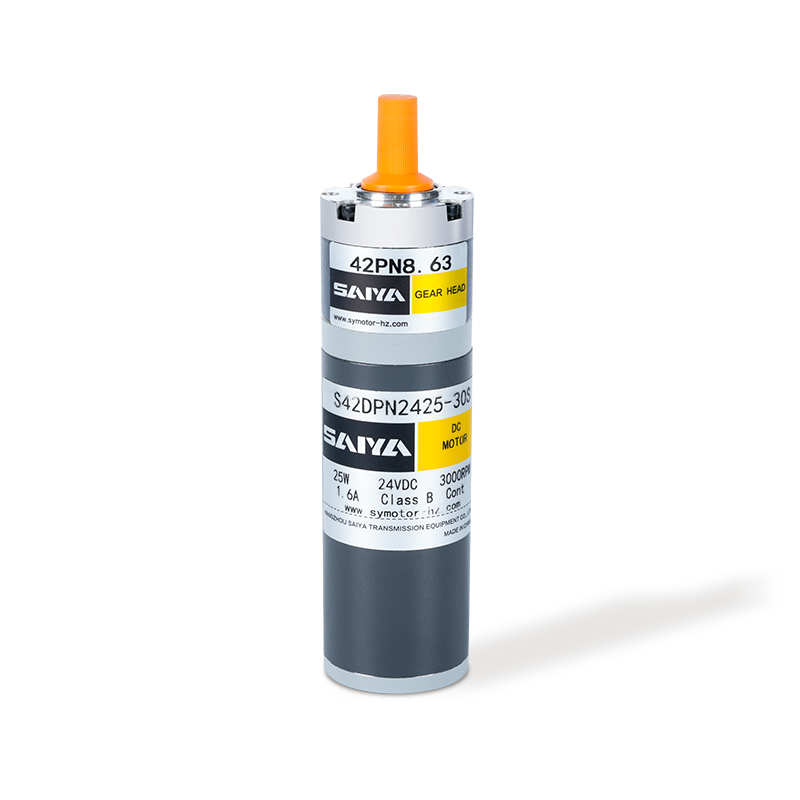
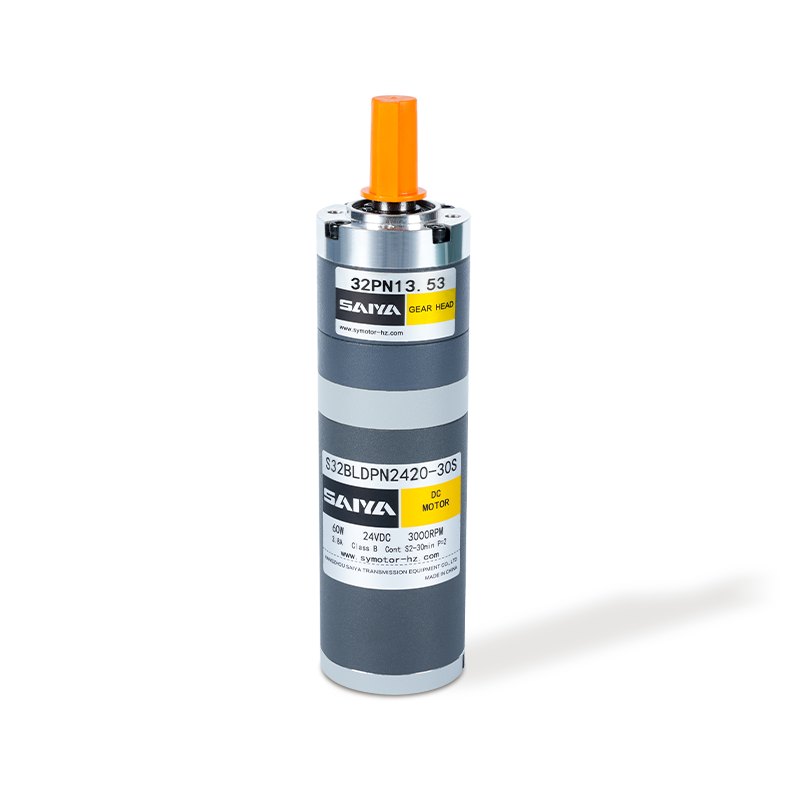
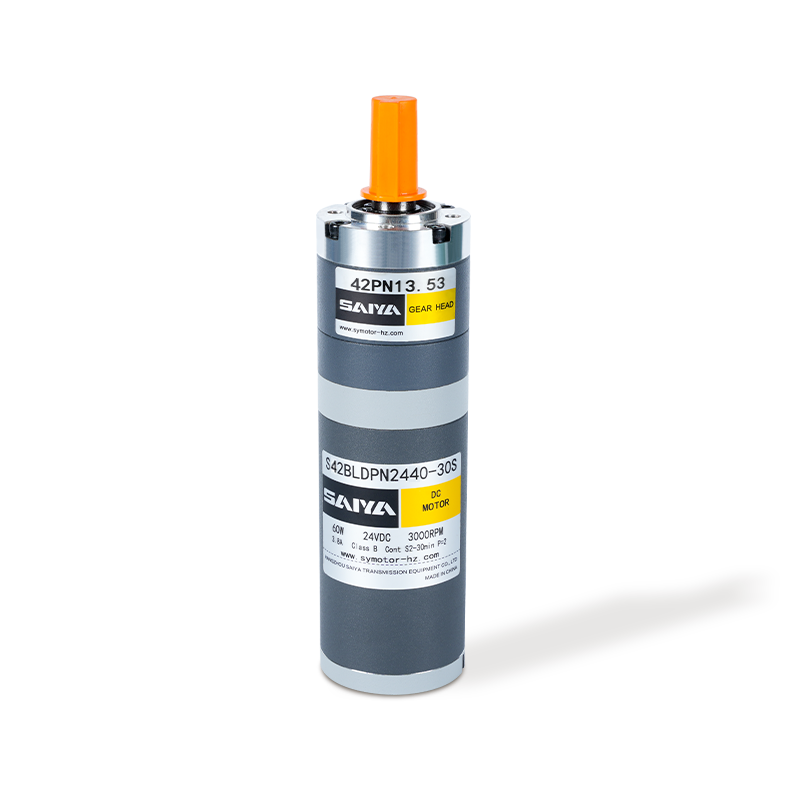
Brushed DC gear motors consist of several key components: a stator, a rotor, brushes, a commutator, and a gearbox. The stator, typically made of permanent magnets or electromagnetic coils, creates a fixed magnetic field. The rotor, comprising coils wound around an armature, rotates within this field. Brushes, fixed at one end of the stator, serve as electrical contacts that transfer current to the rotor's coils via the commutator.
The commutator is a mechanical switch attached to the rotor's shaft, with segments that make and break contact with the brushes as the rotor rotates. This contact reversal ensures that the current through the rotor coils alternates, maintaining the magnetic field's direction and enabling continuous rotation. The gearbox, attached to the rotor's shaft, reduces the motor's speed and increases its torque, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control and high torque outputs.
Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness: Brushed DC gear motors are relatively inexpensive due to their simple construction and control circuits. This makes them an attractive choice for cost-sensitive applications.
Linear Speed-Torque Relationship: The motors' speed is directly proportional to the applied voltage, and the torque is proportional to the current. This characteristic allows for precise control of both speed and torque.
Ease of Control: Basic brushed DC gear motors require only two cables between the power source and the motor, simplifying wiring and reducing costs associated with connectors and cables.
Widespread Applications: From cheap electronic toys and fans to automotive seat adjusters, brushed DC gear motors find their way into numerous devices, testament to their versatility.
Disadvantages
Brush Wear: The brushes and commutator are prone to wear and tear, requiring periodic replacement, which increases maintenance costs.
Electromagnetic Interference: Sparks generated between the brushes and commutator can cause electromagnetic interference, potentially affecting other system components.
Limited Lifespan: Brush wear limits the motor's overall lifespan. Additionally, high currents can cause magnetic material to demagnetize, further degrading performance.
Lower Efficiency: Friction and heat losses at the brush contacts reduce the motor's efficiency compared to brushless DC motors.
Despite their limitations, brushed DC gear motors continue to evolve. Innovations in winding designs, such as the introduction of wave windings alongside stacked windings, have reduced copper usage, lowering costs and weight while maintaining performance. Manufacturers are also exploring materials and coatings to extend brush and commutator lifespan, thereby improving reliability and reducing maintenance requirements.


 EN
EN  English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español